Procedural types


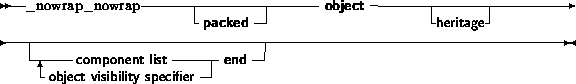
Free Pascal has support for procedural types, although it differs a little from the Turbo Pascal implementation of them. The type declaration remains the same, as can be seen in the following syntax diagram:
Procedural types
For a description of formal parameter lists, see chapter (![]() ).
).
The two following examples are valid type declarations:

One can assign the following values to a procedural type variable:
Given these declarations, the following assignments are valid:
![]()
From this example, the difference with Turbo Pascal is clear: In Turbo
Pascal it isn't necessary to use the address operator (@)
when assigning a procedural type variable, whereas in Free Pascal it is required
(unless you use the -So switch, in which case you can drop the address
operator.)
Remark that the modifiers concerning the calling conventions (cdecl,
pascal, stdcall and popstack stick to the declaration;
i.e. the following code would give an error:

Because the TOneArgCcall type is a procedure that uses the cdecl
calling convention.
At the moment, the method procedural pointers (i.e. pointers that point to methods of objects, distinguished by the of object keywords in the declaration) are still in an experimental stage.